Welcome to our comprehensive guide on tent setup! Properly setting up your tent ensures safety, comfort, and durability․ Start by selecting a flat, dry spot and using a tarp for ground protection․ Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to avoid damage and ensure a secure structure․ This guide will walk you through essential steps to make your camping experience enjoyable and stress-free․
1․1 Choosing the Right Location for Your Tent
Selecting the right location is crucial for a safe and comfortable camping experience․ Look for a flat, dry area free from rocks, branches, and standing water․ Avoid low-lying spots to prevent water accumulation․ Clear the site of debris and sharp objects to protect the tent floor․ Ensure the area is level and stable to maintain structural integrity․ If camping in a designated site, use the provided tent pad․ Consider wind direction to position the tent for optimal ventilation and stability․

1․2 Unpacking and Organizing Components
Start by unpacking all tent components, including poles, stakes, rainfly, and footprint․ Lay them out on a clean, dry surface to ensure nothing is missing or damaged․ Identify each part by referring to the manual or product page․ Organize poles by length and type, and separate stakes from other hardware․ Prepare the footprint or tarp to lay the tent body on, ensuring a smooth setup process․ Double-check for any missing items before proceeding to avoid delays during assembly․
Understanding Tent Components
Familiarize yourself with tent fabric, poles, stakes, rainfly, and footprint․ The fabric provides structure and weather protection, while poles form the frame․ Stakes secure the tent, the rainfly adds extra waterproofing, and the footprint protects the base from moisture and abrasion․
2․1 Identifying Tent Fabric, Poles, and Stakes
Identify the tent fabric, poles, and stakes before assembly․ The fabric is typically waterproof and durable, while poles are lightweight yet sturdy, made of materials like aluminum or fiberglass․ Stakes, usually metal or plastic, secure the tent to the ground․ Familiarizing yourself with these components ensures proper setup and structural integrity․ Each part plays a crucial role in maintaining the tent’s stability and weather resistance, so inspect them for damage before use․
2․2 Familiarizing Yourself with the Rainfly and Footprint
Familiarize yourself with the rainfly and footprint, essential components for weather protection․ The rainfly is a waterproof layer placed over the tent, while the footprint is a protective barrier beneath it, shielding the tent floor from moisture and abrasion․ Both enhance durability and comfort․ Ensure the rainfly is securely attached to the tent’s poles and the footprint aligns perfectly with the tent’s base for optimal performance and longevity․

Step-by-Step Assembly Guide
Begin by laying out the footprint and tent body․ Attach poles to corners, stand the tent upright, and secure with stakes․ Follow instructions carefully for a sturdy setup․
3․1 Preparing the Site and Laying Out the Footprint
Start by selecting a flat, dry area, clearing debris like rocks or branches․ Lay a tarp or footprint to protect the tent floor from moisture and damage․ Ensure the site is level and free of sharp objects that could puncture the tent․ Position the footprint evenly, aligning it with the tent body for proper fit․ This step ensures a stable base for the tent, preventing water pooling and enhancing durability․ Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for site preparation․
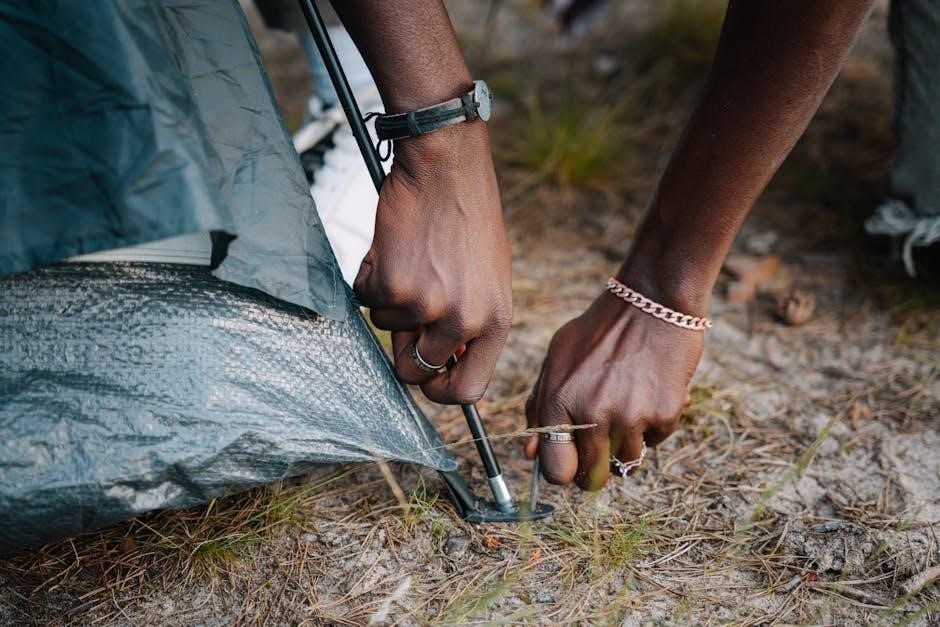
3․2 Attaching the Tent Body to the Poles
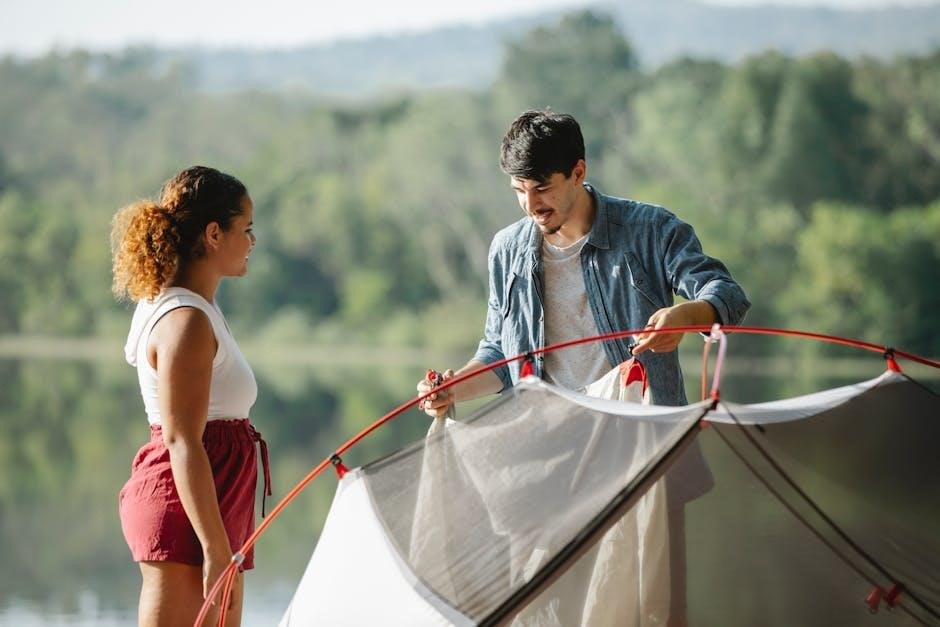

Locate the grommets or pole sleeves on the tent body and align them with the corresponding poles․ Insert the pole tips into the grommets, ensuring they fit securely․ For color-coded systems, match the poles to the sleeves for proper alignment․ Attach the clips or hooks on the tent body to the poles, working from the bottom up․ Ensure the tent stands upright and the fabric is taut but not overly tight․ Repeat for all poles, then move on to securing the structure with stakes․
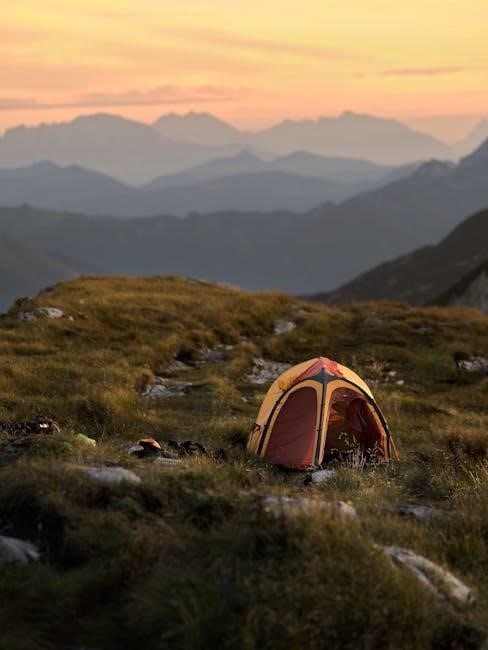
3․3 Raising the Tent and Securing with Stakes
Once the poles are attached, carefully stand the tent upright․ Ensure all corners are aligned and the structure is balanced․ Insert stakes through the stake loops at the base of the tent and hammer them firmly into the ground․ Start with the four corners, then move to the sides, tightening the fabric as you go․ Use a mallet to secure the stakes deeply for stability․ Check that the tent is level and the fabric is taut but not overly strained․ Periodically inspect the stakes to ensure they remain secure, especially in windy or wet conditions․
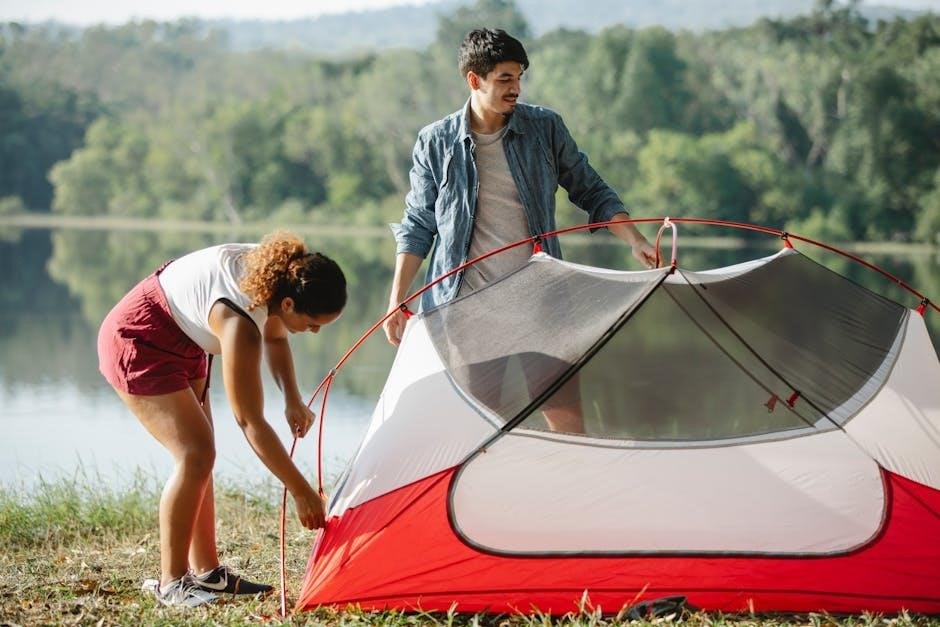

Securing and Tightening Your Tent
Stake the tent firmly at each corner, ensuring the fabric is tight․ Use ropes to secure the rainfly and tighten all connections․ Check for any slack or sagging areas and re-stake if necessary to maintain stability and weather resistance․
4․1 Properly Staking and Tightening the Tent Fabric
Properly staking and tightening the tent fabric is crucial for stability and weather resistance․ Start by driving stakes into the ground at a 45-degree angle to secure the tent corners․ Ensure the fabric is tight and evenly spread, with no sagging areas․ Use the provided ropes and tensioners to tighten the fabric around the poles․ Check each stake and rope connection to ensure they are firmly in place, preventing any looseness that could compromise the tent’s structure during wind or rain․
4․2 Attaching and Adjusting the Rainfly
Attach the rainfly by clipping or hooking it to the tent’s pole ends, ensuring it covers the entire roof․ Adjust the rainfly tightly to prevent sagging, using the provided straps or toggles․ Secure the rainfly edges to the tent stakes, ensuring proper alignment and even tension․ Check for any gaps or loose areas to maintain weather resistance․ Tighten all connections firmly to guarantee the rainfly stays in place during wind or rain, providing optimal protection for your tent․

Maintenance and Storage Tips
Regularly clean and dry your tent to prevent mold and mildew․ Store it in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight․ Avoid harsh chemicals and ensure all components are securely packed to maintain durability and performance for future use․
5․1 Cleaning and Drying the Tent
Regular cleaning and proper drying are essential for maintaining your tent’s longevity․ Start by brushing off loose dirt and debris․ For tougher stains, use a mild soap and warm water, avoiding harsh chemicals that can damage the fabric․ Rinse thoroughly and allow the tent to air dry completely, ensuring no moisture remains․ Never store a damp tent, as this can lead to mold and mildew growth, compromising its water resistance and overall integrity․ Always follow the manufacturer’s cleaning guidelines to preserve your tent’s condition and performance for future camping trips․

Additional Accessories for Enhanced Setup
Enhance your tent setup with essential accessories like tarps, footprints, and gear lofts․ These additions protect your tent, organize gear, and improve overall camping comfort and functionality․
6․1 Using a Tarp or Footprint
A tarp or footprint is essential for protecting your tent from moisture and abrasion․ Lay it flat on the ground before setting up your tent to create a barrier․ Ensure the tarp is slightly smaller than the tent floor to prevent water pooling․ This extra layer not only extends the life of your tent but also makes cleanup easier․ Always check the manufacturer’s size recommendations for the best fit and durability․
6․2 Incorporating Gear Lofts or Vestibules
Gear lofts and vestibules are excellent additions to enhance your tent’s functionality․ Gear lofts provide overhead storage for small items, keeping your tent organized and clutter-free․ Vestibules extend your tent’s footprint, offering a protected area for boots and gear․ Both are easy to attach and can significantly improve your camping experience by maximizing space and keeping essentials dry and accessible․ They are ideal for campers seeking extra storage without compromising tent performance․
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
Ensure your tent’s longevity and safety by avoiding prolonged UV exposure, maintaining proper ventilation, and keeping the area clear of sharp objects and hazards․
7․1 Avoiding Overexposure to UV Rays
Protect your tent from prolonged UV exposure to prevent material degradation and discoloration․ Select shaded areas when possible and avoid leaving your tent set up for extended periods․ Use UV-resistant tarps or covers for added protection․ Regularly inspect fabric for signs of wear, and ensure proper ventilation to reduce heat buildup․ Follow manufacturer guidelines for UV protection to maintain your tent’s durability and performance over time․
7․2 Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining a dry and comfortable tent environment․ Always ensure windows and vents are open to allow airflow, reducing moisture buildup․ Use the rainfly correctly to protect against rain while keeping the tent breathable․ Avoid fully sealing the tent, as this can trap condensation and lead to mold․ Regularly inspect and clean vents to ensure optimal airflow․ Proper ventilation prevents internal humidity and extends the lifespan of your tent, ensuring a pleasant camping experience․

Disassembly and Packing Up
Disconnect poles, remove stakes, and gently fold the tent․ Clean and dry all components before storage․ Organize parts in the storage bag for future use․
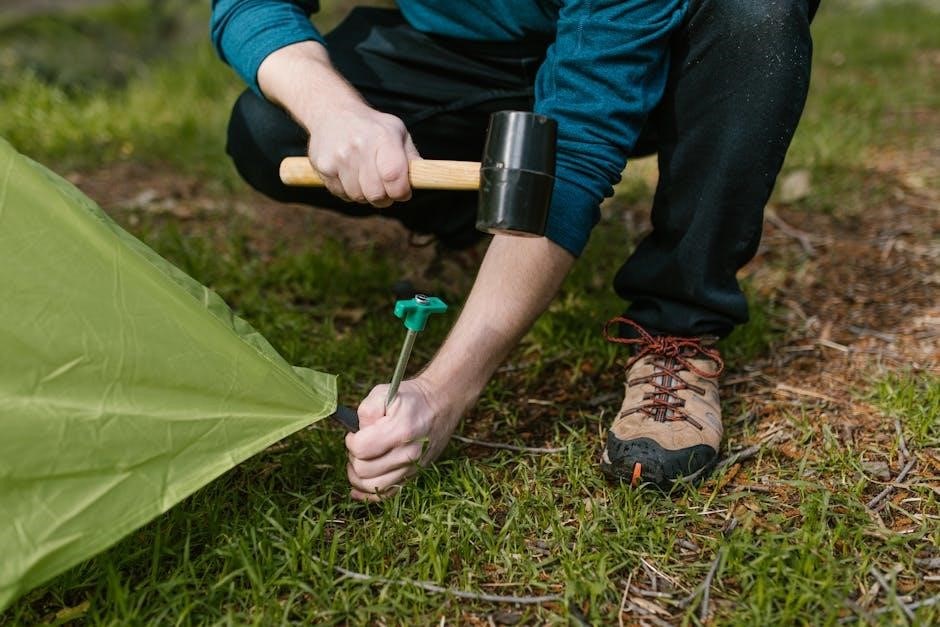
8․1 Dismantling the Tent Safely
Begin by removing all stakes and ropes to prevent damage․ Carefully disengage poles from the tent body, starting from the back and working towards the front․ Avoid abrupt movements that could bend or break the poles․ Once the tent is completely dismantled, inspect each component for wear or damage․ Store poles and stakes separately to maintain organization and prevent loss․ Clean and dry all parts before packing to ensure longevity and prevent mildew․
8․2 Organizing and Storing Components
After dismantling, clean and dry all components thoroughly to prevent mildew․ Store poles, stakes, and tent body in separate, labeled storage bags for easy access․ Use the original packaging or sturdy containers to protect items during storage․ Keep the tent manual and repair kit with the tent for future reference․ Ensure all parts are completely dry before storing to maintain quality and prevent damage․ Store in a cool, dry place to preserve the tent’s condition for future use․

Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identify and address common tent issues like broken poles, water leakage, or torn fabric․ Use repair kits for quick fixes and consult the manual for detailed solutions․
9․1 Fixing Broken Poles or Damaged Fabric
Assess the damage to poles or fabric and use repair tools from the tent kit․ For broken poles, apply a splint or ferrule to stabilize the break, securing with tape․ If fabric is torn, clean the area and apply a patch kit or waterproof adhesive․ Allow repairs to dry before continuing setup․ Regular maintenance and proper storage can prevent such issues․ Always refer to the manual for specific repair instructions tailored to your tent model․
9․2 Addressing Water Leakage or Condensation
Inspect the tent for water leakage by checking seams and fabric for damage․ Apply a waterproof sealant or repair tape to affected areas․ For condensation, ensure proper ventilation by opening windows and vents․ Pitch the tent on a well-drained site to reduce moisture accumulation․ Regularly cleaning and drying the tent can prevent mold and mildew․ Addressing these issues promptly will maintain the tent’s performance and extend its lifespan․ Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for repairs and maintenance․